Artificial Intelligence | ||||||
|
|
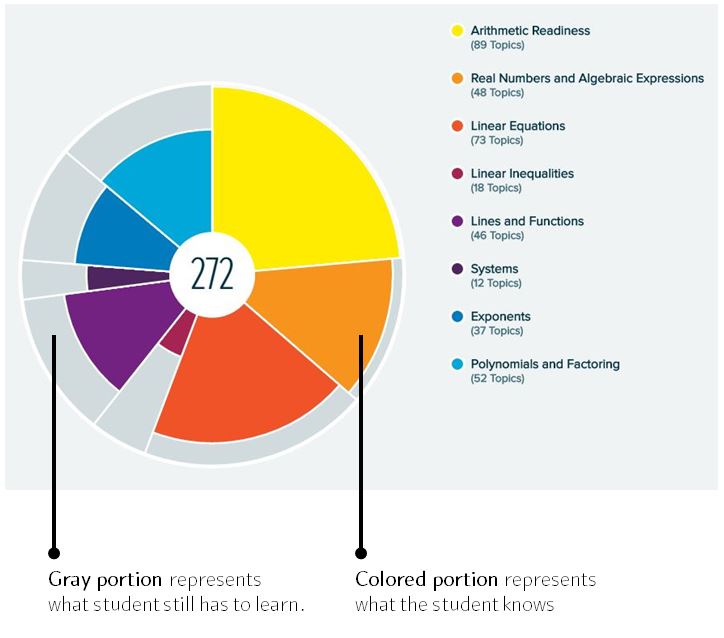
ALEKS Adaptive LearningAt the end of the assessment, the student proceeds into the ALEKS Learning Mode, where she is given a list of topics that she is ready to learn. The concept of ready to learn is critical because this is where the student’s learning progress takes place: learning proceeds by mastering a new topic in the ALEKS "ready to learn," creating a new knowledge state. The new knowledge state has its own ready to learn, and so forth. The student's knowledge is represented by a multicolor pie chart, which also serves as a user-friendly student navigation tool and a powerful motivator. See Figure 5 below. Figure 5
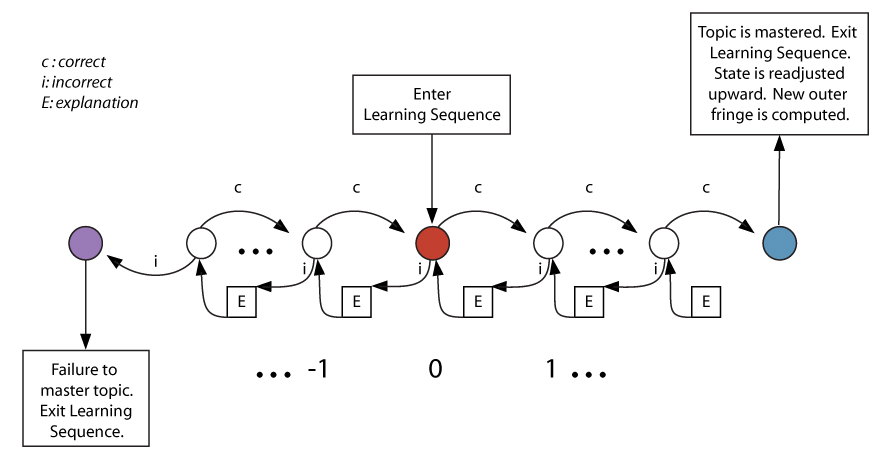
With ALEKS, learning takes place step-by-step, one topic at a time. The student chooses a topic in the ALEKS Learning Mode, which initiates a learning sequence illustrated by Figure 6. ALEKS monitors the sequence of successes and failures of the student in attempting to solve the problem and understand the explanation, and guides the student's progress.
Figure 6 The student enters the system at the red dot and is given an instance of the problem. The student is given an explanation [E] of the solution in certain cases of a failure to solve an instance or whenever she clicks on "Explain." When the student gives a correct response to an instance, a new instance is given. When a sufficiently long sequence of instances is observed 4, ALEKS may decide that the problem has been learned and the student will then leave the system at the blue dot. The knowledge state of the student is then adjusted upward. Empirical data derived from millions of students over more than 12 years reflects a success rate greater than 90% when ALEKS determines that a student is "ready to learn" a particular topic. Each problem type has an extremely large number of specific instances. These instances are algorithmically generated by ALEKS – randomizing numerical values and other problem parameters as each new question (and its explanation) is generated. Each time a student masters an additional topic, ALEKS immediately updates the student’s knowledge state and provides the student with a new list of topics that he is ready to learn. The result is a continuous re-optimization of the student’s learning path.
4 The length of that sequence depends on the context and the student’s behavior. ALEKS models such a sequence as a type of stochastic process. |